Difference between revisions of "JAN 26"
From Alfino
Jump to navigationJump to searchm |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | == | + | ==4. JAN 26== |
| − | ===Assigned=== | + | ===Assigned Work=== |
| − | :* | + | :*Sonnenbergs, C 6, "A Gut Feeling" |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ===In-class | + | ===In-class=== |
| − | :* | + | :*Practicality: Comments on food budgets |
| − | :* | + | :*Satisfcation/Practicality: A 50cent egg lesson |
| − | === | + | ===Practicality: Comments on Food Budgets=== |
| − | :* | + | ::*Some country comparisons: [https://www.ers.usda.gov/data-products/ag-and-food-statistics-charting-the-essentials/food-prices-and-spending/]. Generally, American's spend under 10% of disposable income on food vs. about 14-17% for Italians, French, etc. These are rough comparisons because of wealth effects and geographic effects. Norwegians are wealthier than Americans, Italians a bit less wealthy, but Mediterranean cultures have closer access to inexpensive fresh food. |
| + | ::*Still, at $20/hr, if you spend 14% of net monthly income on food, you would have about $400 to spend. | ||
| − | === | + | ===Satisfaction/Practicality: A 50cent Egg Lesson=== |
| − | :*A | + | :*The original 50cent egg lesson. |
| + | :*A new 50cent egg lesson. | ||
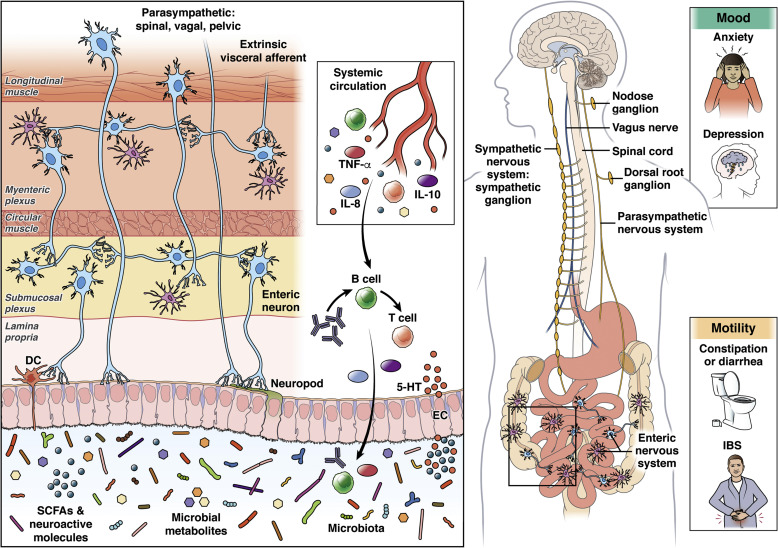
| − | + | ===The Enteric-Central Nervous System Axis=== | |
| − | |||
| − | : | + | [[file:Microbiota-gut-Brain image1.jpg]] |
| − | : | + | [[file:Microbiota-gut-Brain image2.jpg]] |
| − | + | ===Sonnenbergs, C 6, "A Gut Feeling"=== | |
| − | + | :*documents the two-way comm bt brain and gut (enteric nervous system). Gut brain is "listening" in on the trillions of microbes in the gut. | |
| − | + | :*Central nervous system (sympathetic and parsympathetic). Autonomic functions like heart rate include "transit rate" of food, secretion of acid in stomach and mucus in intestines. Hypothalmoic-ituitary adrenal axis (HPA) controls hormones that affect digestion. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | :* | + | :*Gut bacteria can influence our perception of the world and behavior: |
| + | ::*serotonin production | ||
| + | ::*toxplasma gondii (rodents and cats) | ||
| + | ::*microbe free mice are bigger risk takers. Critical phase in correcting for this. | ||
| + | ::*mice with impaired microbiota had worse memory (141) | ||
| − | :* | + | :*Speculate symbiotic relationship -- microbes likely improve fitness through risk aversion and memory. |
| + | :*Mechanisms -- gut bacteria produce chemicals that go into blood stream. | ||
| − | ::* | + | :*More evidence of effects on perception and behavior: |
| + | ::*2011 McMaster study: fecal transplants between anxious and gregarious strains of mice partially reversed behavior. Brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF) - associated with depression, schizophrenia, and OCD. Gregarious mice has increase in BDNF after transplant. Intermediate mechanisms not completely clear. | ||
| − | + | :*144: MACS (microbiotically available carbs) produce SCFAs, but also many other compounds, including toxins that normal kidneys filter. Lots to learn. Some stimulate appetite. Many products may be netural with respect to fitness. | |
| − | :* | + | :*hepatic encephalopathy -- treatments target microbes that produce toxins. |
| − | :* | + | :*TMAO - trimethylamine-N-oxide. produced by microbes. implicated in cardiovascular disease. Red meat and fatty foods increase TMAO. Vegans and vegetarians have low TMAO production. Study on long term vegan who eats a steak. Still low TMAO. Might be lacking those microbes. (might argue for low meat consumption as nearly healthful as abstinance). |
| − | ::* | + | :*Two-way communication between "brains" |
| + | ::*induce stress in mice and their microbiota change. threat slows motility and digestion. (maybe prep for action) | ||
| + | ::*some stress events have long term effect on microbiota. 150 | ||
| + | ::*IBS - read - could be a stress induced imbalance that is hard to correct. also heightened pain perception! Some evidence in animal models that probiotics can help. Some studies in humans suggest this as well. Better studies needed. | ||
| + | ::*ASD - autism spectrum disorders. Increasing dramatically. [https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/autism/data.html] Note connection to rise of industrial diets! | ||
| + | ::*ASD research 2013 Caltech studies by Mazmanian - looked at maternal immune response to infection during pregnancy. Treatment with b. fragilis helped somewhat in mice. Effect might involve other microbes. B. fragilis affected over 100 other compounds in blood. Human/mice diffs are significant here. Caution. | ||
| − | : | + | ::*2013 UCLA fMRI study on probiotic yogurt and response to negative facial emotions. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | :* | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 22:44, 26 January 2022
Contents
4. JAN 26
Assigned Work
- Sonnenbergs, C 6, "A Gut Feeling"
In-class
- Practicality: Comments on food budgets
- Satisfcation/Practicality: A 50cent egg lesson
Practicality: Comments on Food Budgets
- Some country comparisons: [1]. Generally, American's spend under 10% of disposable income on food vs. about 14-17% for Italians, French, etc. These are rough comparisons because of wealth effects and geographic effects. Norwegians are wealthier than Americans, Italians a bit less wealthy, but Mediterranean cultures have closer access to inexpensive fresh food.
- Still, at $20/hr, if you spend 14% of net monthly income on food, you would have about $400 to spend.
Satisfaction/Practicality: A 50cent Egg Lesson
- The original 50cent egg lesson.
- A new 50cent egg lesson.
The Enteric-Central Nervous System Axis
File:Microbiota-gut-Brain image1.jpg
Sonnenbergs, C 6, "A Gut Feeling"
- documents the two-way comm bt brain and gut (enteric nervous system). Gut brain is "listening" in on the trillions of microbes in the gut.
- Central nervous system (sympathetic and parsympathetic). Autonomic functions like heart rate include "transit rate" of food, secretion of acid in stomach and mucus in intestines. Hypothalmoic-ituitary adrenal axis (HPA) controls hormones that affect digestion.
- Gut bacteria can influence our perception of the world and behavior:
- serotonin production
- toxplasma gondii (rodents and cats)
- microbe free mice are bigger risk takers. Critical phase in correcting for this.
- mice with impaired microbiota had worse memory (141)
- Speculate symbiotic relationship -- microbes likely improve fitness through risk aversion and memory.
- Mechanisms -- gut bacteria produce chemicals that go into blood stream.
- More evidence of effects on perception and behavior:
- 2011 McMaster study: fecal transplants between anxious and gregarious strains of mice partially reversed behavior. Brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF) - associated with depression, schizophrenia, and OCD. Gregarious mice has increase in BDNF after transplant. Intermediate mechanisms not completely clear.
- 144: MACS (microbiotically available carbs) produce SCFAs, but also many other compounds, including toxins that normal kidneys filter. Lots to learn. Some stimulate appetite. Many products may be netural with respect to fitness.
- hepatic encephalopathy -- treatments target microbes that produce toxins.
- TMAO - trimethylamine-N-oxide. produced by microbes. implicated in cardiovascular disease. Red meat and fatty foods increase TMAO. Vegans and vegetarians have low TMAO production. Study on long term vegan who eats a steak. Still low TMAO. Might be lacking those microbes. (might argue for low meat consumption as nearly healthful as abstinance).
- Two-way communication between "brains"
- induce stress in mice and their microbiota change. threat slows motility and digestion. (maybe prep for action)
- some stress events have long term effect on microbiota. 150
- IBS - read - could be a stress induced imbalance that is hard to correct. also heightened pain perception! Some evidence in animal models that probiotics can help. Some studies in humans suggest this as well. Better studies needed.
- ASD - autism spectrum disorders. Increasing dramatically. [2] Note connection to rise of industrial diets!
- ASD research 2013 Caltech studies by Mazmanian - looked at maternal immune response to infection during pregnancy. Treatment with b. fragilis helped somewhat in mice. Effect might involve other microbes. B. fragilis affected over 100 other compounds in blood. Human/mice diffs are significant here. Caution.
- 2013 UCLA fMRI study on probiotic yogurt and response to negative facial emotions.