Difference between revisions of "Philosophy of Human Nature Lecture Notes"
| Line 139: | Line 139: | ||
==1/29/2009== | ==1/29/2009== | ||
| − | + | --Review terms in Epistemology | |
===Skepticism=== | ===Skepticism=== | ||
Revision as of 17:13, 3 February 2009
Return to Human Nature main page.
We'll use this page to post supplemental material to our class sessions. - Alfino
1/13/2009: Course Intro
- Course Goals
- Roll Call
- Schedule, Grading Schemes, Wiki, Journals, Study Questions
- Philosophy
Identifying the Philosophical
- Turn toward basic questions
- Meta-level cognition in general - theorizing
- In the Structure of Knowledge
Note to Class
Thanks for a good first class. Please go through your "to do" list from class and let me know if you have any difficulties.
Also, here's your first journal assignment: For Thursday: After reading the excerpt from the Apology, summarize in one or two paragraphs the main charges against Socrates and his defense. Select a detail or two that you find particularly interesting. Then make a brief (one paragraph) assessment of Socrates defense. End with one or two questions you still have after reading the passage. 1 - 1.5 pages, typed, double spaced.
1/15/2009
What is Real? (1st Exercise)
What is Philosophy?
- Philosophy is a discipline of inquiry directed toward a wide range of basic questions about the nature of the universe and our experience in it. It involves a turn toward "basic questions". It also involves meta-level cognition.
Logos, Mythos, and Theos
- locating philosophy in relation to Mythos and Theos
Other ways of identifying Philosophy
- in relation to science
- as speculative
- as dealing with matters of direct importance to living
- as dealing with matters of great uncertainty
Philosophical Methods
Go to Philosophical Methods
1/20/2009
Introduction to Platonic Metaphysics
Plato's answer to the question, "What is Real?"
- The real is what persists through all changes and manifestations.
Rationality and the Project of Essential Definition
- Through the project of giving essential definiutions (relentlessly asking, "What makes all instances of X (horses) "X" (capable of having the word "horse" predicated of it), Plato is led to focus on form as persistent reality.
Allegory of the Cave
- The Allegory of the Cave gives us an image of the implications of Plato's metaphysics for his view of human existence.
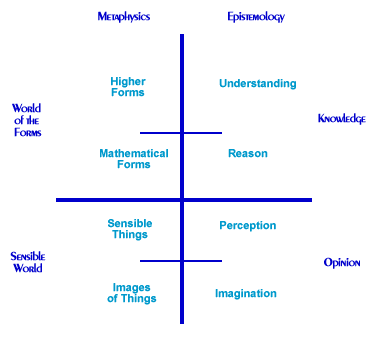
Divided Line
1/22/2009
Some Notes on Greek History, or, How did we ever get to the Apology?
More Really Important Dates
- 2220 bc Creatan Minoan Culture
- 1000 bc Destruction of Mycenean Palace Culture
- 900-800 revival of population on Peloponesis, use of iron in tools and weapons.
- 750 city states growth.
- 750-550 period of Greek colonization.
- 480 Xerxes, ruler of Persia attacks at Thermopylae and Salamis
- 477, Athens governs Delian League
- 495-429, Pericles.
- 450-429, Period of "Periclean Athens" - democratic and legal reforms. great playwrights such as: Sophocles, Aeschylus, and Euripides
- 431-404, Peloponnesian War, starting with Spartan invasion of Attica, ending with Athens surrender in 404
- 415, Alcibiades defects to Sparta.
- 404, Athens surrenders to Sparta.
- 404-403, Reign of Terror, 30 Tyrants.
- 399, Socrates trial.
1/27/2009
Part One: Initial Three Speeches of Symposium
The main focus of today's class will be the three speeches on love by Phaedrus, Pausanias and Eryximachus, from the Symposium.
Phaedrus:
Pausanias:
Erixymachus:
What kind of thing is love, should it be praised, and if so, how? For motivating us to virtue? Is love about intimate relationship (sexual or not) or is it a broader force in the universe?
Exercise: Beginning your theory of the value of love.
Part Two: Introduction to Epistemology
Types of Knowledge
- Propositional, Know-how, Knowledge by acquaintance
Defining Knowledge as "true, justified belief"
Skepticism, Empiricism, and Rationalism
Skepticism
1/29/2009
--Review terms in Epistemology
Skepticism
- Could There be another world "behind" or "alongside" this one, as in the Matrix?
- Could I be radically wrong about my knowledge of this world?
Love: Aristophanes, theorizing without Plato
- Aristophanes' speech: summary
- Try leaving Plato aside and start theorizing about love from your current knowledge and reasonable inferences.
- A naturalist starting point for love
- Love as a "quasi-universal," but variable product of human culture, based in our organic drives and evolved cognitive and affective structures.
- Consider theoretical possibilities, Could I be radically wrong about this? What questions does it answer or leave unanswered?
- The "normativity" of reason.
Show parabola video if there is time.[1]
2/3/2009
-study question review, roll call question, grading schemes.
Part A: Socrates Questioning of Agathon in Symposium
- Is Love love of something?
- Does love desire that of which it is the love?
- When we desire something, do we possess it? likely vs. necessarily?
- IC: If soemthing needs beauty and does not have it, one cannot be beautiful.
Love is not possession, but the desire of the beloved. Or the desire of the continuation of the love.
philosophia vs. sophia
Part B: Scepticism and Foundations of Certainty
review of Descartes' 1st Mediation, looking to Meditation 2.
2/5/2009
2/10/2009
2/12/2009
2/17/2009
2/19/2009
2/24/2009
2/26/2009
3/3/2009
3/5/2009
3/17/2009
3/19/2009
3/24/2009
3/26/2009
3/31/2009
4/2/2009
4/7/2009
4/9/2009
4/14/2009
4/16/2009
4/21/2009
4/23/2009
4/28/2009
4/30/2009
5/8/2009
Old Material: