Philosophy of Human Nature Lecture Notes
Return to Human Nature main page.
We'll use this page to post supplemental material to our class sessions. - Alfino
1/13/2009: Course Intro
- Course Goals
- Roll Call
- Schedule, Grading Schemes, Wiki, Journals, Study Questions
- Philosophy
Identifying the Philosophical
- Turn toward basic questions
- Meta-level cognition in general - theorizing
- In the Structure of Knowledge
Note to Class
Thanks for a good first class. Please go through your "to do" list from class and let me know if you have any difficulties.
Also, here's your first journal assignment: For Thursday: After reading the excerpt from the Apology, summarize in one or two paragraphs the main charges against Socrates and his defense. Select a detail or two that you find particularly interesting. Then make a brief (one paragraph) assessment of Socrates defense. End with one or two questions you still have after reading the passage. 1 - 1.5 pages, typed, double spaced.
1/15/2009
What is Real? (1st Exercise)
What is Philosophy?
- Philosophy is a discipline of inquiry directed toward a wide range of basic questions about the nature of the universe and our experience in it. It involves a turn toward "basic questions". It also involves meta-level cognition.
Logos, Mythos, and Theos
- locating philosophy in relation to Mythos and Theos
Other ways of identifying Philosophy
- in relation to science
- as speculative
- as dealing with matters of direct importance to living
- as dealing with matters of great uncertainty
Philosophical Methods
Go to Philosophical Methods
1/20/2009
Introduction to Platonic Metaphysics
Plato's answer to the question, "What is Real?"
- The real is what persists through all changes and manifestations.
Rationality and the Project of Essential Definition
- Through the project of giving essential definiutions (relentlessly asking, "What makes all instances of X (horses) "X" (capable of having the word "horse" predicated of it), Plato is led to focus on form as persistent reality.
Allegory of the Cave
- The Allegory of the Cave gives us an image of the implications of Plato's metaphysics for his view of human existence.
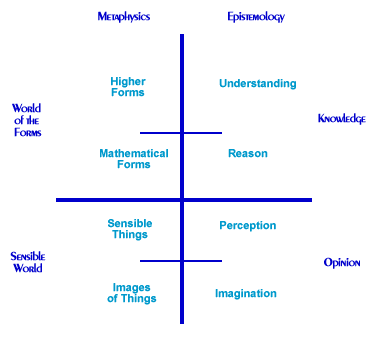
Divided Line
1/22/2009
Some Notes on Greek History, or, How did we ever get to the Apology?
More Really Important Dates
- 2220 bc Creatan Minoan Culture
- 1000 bc Destruction of Mycenean Palace Culture
- 900-800 revival of population on Peloponesis, use of iron in tools and weapons.
- 750 city states growth.
- 750-550 period of Greek colonization.
- 480 Xerxes, ruler of Persia attacks at Thermopylae and Salamis
- 477, Athens governs Delian League
- 495-429, Pericles.
- 450-429, Period of "Periclean Athens" - democratic and legal reforms. great playwrights such as: Sophocles, Aeschylus, and Euripides
- 431-404, Peloponnesian War, starting with Spartan invasion of Attica, ending with Athens surrender in 404
- 415, Alcibiades defects to Sparta.
- 404, Athens surrenders to Sparta.
- 404-403, Reign of Terror, 30 Tyrants.
- 399, Socrates trial.
1/27/2009
The main focus of today's class will be the three speeches on love by Phaedrus, Pausanias and Eryximachus, from the Symposium.
Phaedrus:
Pausanias:
Erixymachus:
What kind of thing is love, should it be praised, and if so, how? For motivating us to virtue? Is love about intimate relationship (sexual or not) or is it a broader force in the universe?
1/29/2009
2/3/2009
2/5/2009
2/10/2009
2/12/2009
2/17/2009
2/19/2009
2/24/2009
2/26/2009
3/3/2009
3/5/2009
3/17/2009
3/19/2009
3/24/2009
3/26/2009
3/31/2009
4/2/2009
4/7/2009
4/9/2009
4/14/2009
4/16/2009
4/21/2009
4/23/2009
4/28/2009
4/30/2009
5/8/2009
Old Material: